Google has been dedicated to increasing security in Android and all its other products. The company’s developers are highly skilled, yet flaws still escape detection. This is where their Vulnerability Rewards Programs (VRPs) come in, with rewards given to anyone who responsibly discloses issues with Google products. 2021 has proven to be a banner year for VRPs, as Google has paid over $12 million across multiple platforms such as Android and Chrome.
In 2022, Google rewarded security researchers with $4.8 million for identifying weaknesses in Android – the highest payout of all time being $605,000. The Chrome program also saw a total of $4 million with the majority being given to Chrome researchers and around half a million going to those who located issues in ChromeOS. The remainder of the money was distributed over other programs, such as Google Play and their new Open Source VRP that provides incentives for anyone uncovering flaws in Google’s open source initiatives.
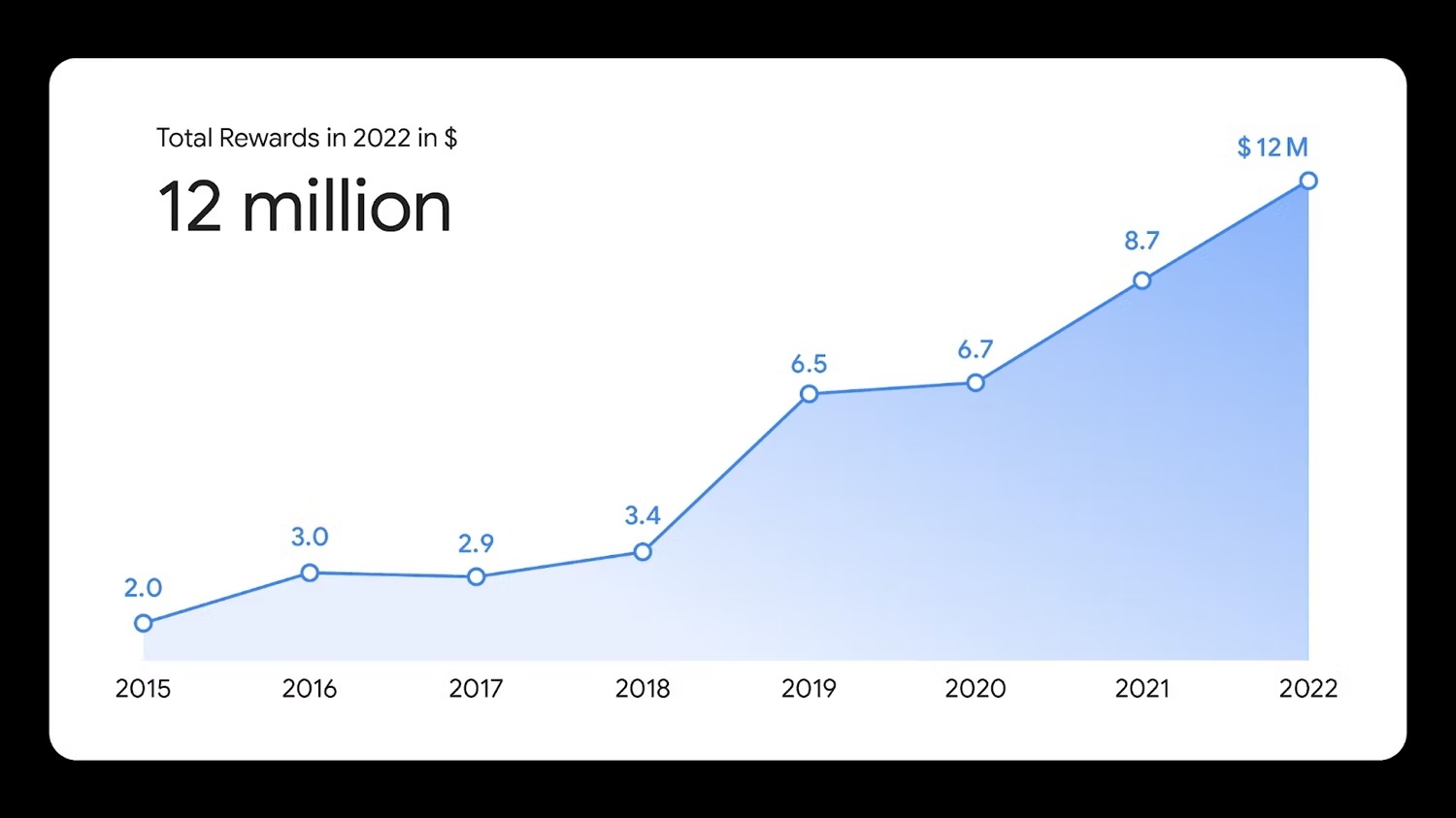
As compared to 2021, last year’s payouts increased from $8.7 million to $12 million. That’s exactly when hackers received from Google $12 million in bounties. This is partly due to the company offering additional incentives and adding more qualifying devices to its list, such as Fitbits and Google Nests. The Open Source program, mentioned earlier, is also likely to have contributed to this.
This year, in 2023, the company wants to offer more experiments within the Chrome program. Those who find bugs and vulnerabilities in Chrome and ChromeOS will receive bonus opportunities and other experiments. More than 20 instructional videos were also added for researchers wanting to disclose issues, making the process easier.
While $12 million might seem like a lot, it was nothing compared to Google’s expected revenue of $280 billion in 2022. As actively exploited vulnerabilities pose a massive risk to the company then any rewards program would ever be able to. That’s why this investment makes so much sense.









